Page 66 - rp-may-2020
P. 66
CPD ACTIVITY 64
RET AIL PHARMA C Y • MA Y 2020
FROM PAGE 63
evidence that vaccinating young children
reduces the amount of carriage in the
population (people who carry the bacteria
in their nose and throat but don’t get sick
from it). This means people not vaccinated
may be protected from the groups of
disease covered by the vaccine. This is
known as herd, or community immunity.
16
The 23vPPV is not administered to
infants. It’s available to children aged
four years who are medically at risk of
contracting pneumonia.
1
MMR and MMRV
MMR vaccine (measles, mumps, rubella)
is a live, attenuated vaccine. The measles
component was first introduced in
1968. MMR vaccine combined was
recommended and funded on the national
schedule for infants in 1989. A second
MMR dose was introduced in 1992 and,
since this period, a second dose has
been funded by various states to ensure
complete immunisation as per the NIP.
4
MMRV (measles, mumps, rubella, varicella)
was funded from 2013 for the second dose
at 18 months.
Measles
Measles is a highly contagious disease
spread by droplet or aerosol. The infection
rate is prolific (see Figure 4). The symptoms
are notably fever and at least one of the
three Cs: cough, coryza (inflammation
of the nasal mucous membrane) and
conjunctivitis. Koplik’s spots appear on
the buccal mucosa as small white papules
and provide an opportunity to clinically
diagnose measles a day or two before the
rash appears.
14
The maculopapular rash appears three
to four days after the onset of symptoms.
It begins on the face, behind the ears and
then tracks down the trunk and extremities.
The rash might be minimal in children
with vaccine-modified measles (who have
previous immunity following vaccination)
and these children might not have cough,
Figure 3.
Chest X-ray of complicated pneumonia showing opacification of the left lung
field consistent with a large pleural effusion and empyema (pus in the pleural cavity).
16
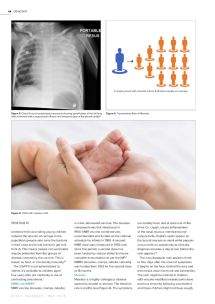
Figure 4.
Transmission Rate of Measles
Figure 5.
Child with measles rash.
A single person with measels infects 9-18 other people on average
Fig 2
Chest x ray of complicated pneumonia showing opacification of the left lung field consistent with a large pleural
effusion and empyema. There is associated right sided bronchial wall thickening and consolidation. The pleural effusion
resolved after chest drain insertion. Group A streptococcus was isolated from pleural fluid
PRACTICE
on 26 April 2020 at Queensland University of Technology. Prohttp://www.bmj.com/BMJ: first published as 10.1136/bmj.j686 on 2 March 2017. Downloaded from