Page 45 - Retail Pharmacy Magazine October 2020
P. 45
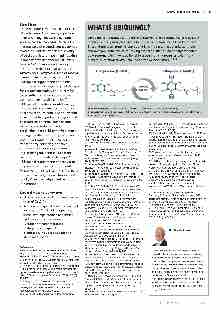
BUSINESS THROUGH INNOVATION LEGAL 43 WHAT IS UBIQUINOL? Ubiquinol is the reduced, and more bioactive, form of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) found in virtually every human cell and critical for healthy cellular function.1-4 This endogenous lipophilic compound is named after its ubiquitous nature and benzoquinone structure, having a benzoquinone ring and hydrophobic polyisoprenoid tail. Two additional hydrogen ions increase its polarity and bioactivity compared with ubiquinone, the oxidised form.2-3, 8, 12 Image subtext: Ubiquinone must be reduced to ubiquinol to function in the body.3 Image source: Lord D, Quigley G. ‘Ubiquinol: Potential therapy for heart diseases and considerations in respiratory comorbidities’. Heart health1-2, 4 The bioenergetic effects of ubiquinol is of fundamental importance, especially in cells with high metabolic demand such as cardiac myocytes.2 Such is the importance that a correlation is seen with myocardial deficiency and the severity of cardiocirculatory impairment.2 Studies in patients with heart failure (HF) show plasma CoQ10 levels are inversely associated with functional status and severity of HF symptoms, such as fatigue, exercise tolerance and dyspnea.2, 8 Ubiquinol supplementation is now considered an important adjunct therapy for patients on statins, particularly for those with chronic heart failure and decreased myocardial function.2 Ubiquinol provides essential energy required for heart muscle function and as a potent antioxidant. The antioxidant action is twofold: protecting myocardial cells against potential damage from oxidants, and reducing oxidant production that could potentially cause damage. Furthermore, supplementation promotes improved cardiovascular relaxation by balancing oxidative and reductive reactions, important in protecting the heart muscle from oxidative or free radical damage.1, 8, 11 Ubiquinol supplementation may also help alleviate specific chronic heart failure symptoms, shown to be inversely related in severity to low plasma CoQ10 levels,2,8 such as fatigue and exercise intolerance.13, 22-23 Key points and summary: • Ubiquinol is the preferred supplement form of CoQ10.2-3 • Adequate ubiquinol is of fundamental importance for all cells, especially those with high metabolic demand such as cardiac myocytes. • A number of factors reduce endogenous ubiquinol production, including ageing and statin medication. References 1. Garrido-Maraver J, Oropesa-Ávila M, Fernández- Vega A, De la Mata A, Delgado Pavón A, De Miguel M, Pérez Calero C, Villanueva Paz M, Cotán D, Sánchez-Alcázar JA. ‘Coenzyme Q10’. Molecular Syndromology, 2014; 5: 187-197. 2. KloerHU,BelardinelliR,RuchongO,Rosenfeldt F. ‘Combining ubiquinol with a statin may benefit hypercholesterolaemic patients with chronic heart failure’. Heart, Lung and Circulation, 2020; 29 (2): 188-195. 3. Zhang Y, Liu J, Chen XQ, Oliver Chen C Y. ‘Ubiquinol is superior to ubiquinone to enhance coenzyme Q10 status in older men’. Food & Function, 2018; 9 (11): 5653-5659. 4. Di Lorenzo A, Iannuzzo G, Parlato A, Cuomo G, Testa C, Coppola M, D’Ambrosio G, Oliviero AD, Sarullo S, Vitale G, Nugara C, Sarullo MF, Giallauria F. ‘Clinical evidence for Q10 coenzyme supplementation in heart failure: From energetics to functional improvement’. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 2020; 9 (5). 5. Dikshit M. ‘Oxidative stress in heart diseases’. 2019. 6. Liguori I, Russo G, Curcio F, Bulli G, Aran L, Della-Morte D, Gargiulo G. Testa G, Cacciatore F, Bonaduce D, Abete P. ‘Oxidative stress, ageing, and diseases’. Clinical Interventions in Ageing, 2018; 13: 757-772. 7. Cloonan SM, Choi AMK. ‘Mitochondria in lung disease’. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 2016; 126 (3): 809-820. 8. Hernández-Camacho JD, Bernier M, López-Lluch G, Navas P. ‘Coenzyme Q10 supplementation in ageing and disease’. Frontiers in Physiology, 2018; 9 (44). 9. Rodick TC, Seibels DR, Babu JR, Huggins KW, Ren G, Mathews ST. ‘Potential role of coenzyme Q10 in health and disease conditions’. Nutrition and Dietary Supplements, 2018; 10: 1-11. 10. Hargreaves IP, Mantle D. ‘Coenzyme Q10 supplementation in fibrosis and ageing’. In Reviews on Biomarker Studies in Aging and Anti-Aging Research, Guest PC, Ed. Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2019: 103-112. 11. Littarru GP, Langsjoen P. ‘Coenzyme Q10 and statins: Biochemical and clinical implications’. Mitochondrion, 2007; 7: S168–S174. 12.Guis S, Mattei JP, Nicoli F, Le Fur Y, Kozak-Ribbens G et al. ‘In vivo and in vitro characterisation of skeletal muscle metabolism in patients with statin-induced adverse effects’. Arthritis Rheum, 2006; 55 (17): 551–7. 13.Mousavi S, Mohammadi V, Foroughi Z. ‘Effect of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on work-related fatigue in nurses: A double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled study’. Fatigue: Biomedicine, Health & Behaviour, 2020; 8 (1): 1-10. 14. Sarmiento A, Diaz-Castro J, Pulido-Moran M, Moreno-Fernandez J, Kajarabille N, Chirosa I, Guisado IM, Javier Chirosa L, Guisado R, Ochoa JJ. ‘Short-term ubiquinol supplementation reduces oxidative stress associated with strenuous exercise in healthy adults: A randomised trial’. BioFactors, 2016; 42 (6): 612-622. 15. Diaz-Castro J, Moreno-Fernandez J, Chirosa I, Chirosa LJ, Guisado R, Ochoa JJ. ‘Beneficial effect of ubiquinol on haematological and inflammatory signalling during exercise’. Nutrients, 2020; 12 (2): 424. 16. Annesley JS, Fisher RP. ‘Mitochondria in health and disease’. Cells, 2019; 8 (7). 17. Picard M, McEwen BS. ‘Psychological stress and mitochondria: A systematic review’. Psychosomatic Medicine, 2018; 80 (2). 18. Riou M, Alfatni A, Charles A-L, Andrès E, Pistea C, Charloux A, Geny B. ‘New insights into the implication of mitochondrial dysfunction in tissue, peripheral blood mononuclear cells, and platelets during lung diseases’. Journal of Clinical Medicin, 2020; 9 (5). 19.‘Psychological stress and mitochondria: A systematic review’. Psychosom Med, 2018; 2 (80): 141–153. 20. ‘Mitochondria as central regulators of neural stem cell fate and cognitive function’. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2019; 20: 34-48. 21. Atri D, Siddiqi HK, Lang J, Nauffal V, Morrow DA, Bohula EA. ‘Covid-19 for the cardiologist: A current review of the virology, clinical epidemiology, cardiac and other clinical manifestations and potential therapeutic strategies’. JACC: Basic to Translational Science, 2020. 22. Mehrabani S, Askari G, Miraghajani M, Tavakoly R, Arab A. ‘Effect of coenzyme Q10 supplementation on fatigue: A systematic review of interventional studies’. Complementary Therapies in Medicine, 2019; 43: 181-187. 23. Pellicori P, Khan MJI, Graham FJ, Cleland JGF. ‘New perspectives and future directions in the treatment of heart failure’. Heart Failure Reviews, 2020; 25 (1): 147-159. By Gerald Quigley. Gerald is a pharmacist and master herbalist based in Melbourne, where he helps patients integrate their medications with appropriate nutritional and supplement interventions. He is a fellow of the Naturopaths and Herbalists Asso- ciation of Australia, a member of the Australian Traditional Medicine Society, and a member of the American Botanical Council His passion is to empower each person to make sensible health decisions and to continually maintain and improve their quality of life, espe- cially as they age. RETAIL PHARMACY • OCT 2020