Page 66 - Demo
P. 66
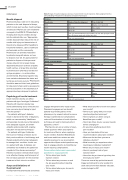
Important referral points • Presence or suspicion of lipohypertrophy. • Patients who have been injecting in areas of lipohypertrophy who will require a dose reduction of insulin when moving to healthy tissue. • Recurrent hypoglycaemia. • Unexplained hyperglycaemia or hypoglycaemia. • Patients with concerns, anxiety or fears regarding injecting insulin. • Patients who exhibit considerable variability in blood glucose readings. • Adherence issues with insulin or other diabetes medicines. Table 2. Insulin injection guide CPD ACTIVITY 65 9. Dunning T. 2014. ‘Care of people with diabetes’. 4th ed. Victoria: Wiley Blackwell. p.506. 10.Frid AH, Hirsch LJ, Gaspar R, Hicks D, Kreugel G, et al. ‘New injection recommendations for patients with diabetes’. Diabetes and Metabolism, 2010; 36 (2): S3-S18. 11. Vaag A, Handberg A, Lauritzen M, Henriksen JE, Pedersen KD, et al. ‘Variation in absorption of NPH insulin due to intramuscular injection’. Diabetes Care, 1990; 13 (1): 74-76. 12.Thow J, Home P. ‘Insulin injection technique’.BMJ, 1990; 301 (6742): 3-4. 13.Gibney MA, Arce CH, Byron KJ, Hirsch LJ. ‘Skin and subcutaneous adipose layer thickness in adults with diabetes at sites used for insulin injections: Implications for needle length recommendations’. Curr Med Res Opin, 2010; 26 (6): 1519-1530. 14.Zambanini A, Newson RB, Maisey M, Feher MD. ‘Injection related anxiety in insulin-treated diabetes’. Diabetes Res Clin Pract, 1999; 46 (3): 239-246. 15. Hunt LM, Valensuela MA, Pugh JA. ‘NIDDM patients’ fears and hopes about insulin therapy: The basis of patient reluctance’. Diabetes Car, 1997; 20 (3): 292-298. 16.Nakatani Y, Matsumura M, Monden T, Aso Y, Nakamoto T. ‘Improvement of glycemic control by re-education in insulin injection technique in patients with diabetes mellitus’. Adv Ther, 2013; 30 (1): 897-906. Accreditation Number: A2007RP1 (exp: 30/06/2022). This activity has been accredited for 1 hour of Group One CPD (or 1 CPD credit) suitable for inclusion in an individual pharmacist’s CPD plan which can be converted to 1 hour of Group Two CPD (or 2 CPD credits) upon successful completion of relevant assessment activities. 1. Which of the following would be the most appropriate recommendation for a 40-year-old adult of normal weight who is administering insulin glargine 10 units at nighttime? A) 4mm needle at a 45-degree angle in the abdomen with a skin fold. B) 4mm needle at a 90-degree angle in the abdomen without a skin fold. C) 8mm needle at a 45-degree angle in the abdomen with no skin fold. D) 8mm needle at a 90-degree angle in the abdomen without a skin fold. 2. What is the recommended insulin needle length for most adults? A) 4mm or 5mm. B) 6mm or 8mm. C) 12mm. D) All lengths are suitable. 3. Which is NOT thought to increase the likelihood of lipohypertrophy? A) Long duration of use of insulin. B) High frequency of insulin administration. C) Lack of insulin site rotation. D) Small total daily dose of insulin. 4. Which of the following in regard to inadvertent intramuscular injection of insulin is INCORRECT? A) Inadvertent intramuscular injection may cause hypoglycaemia with a rapid onset. B) Inadvertent intramuscular injection may be caused by using inappropriately long needles. C) Inadvertent intramuscular injection is more common in the abdomen compared with arm, thigh and buttock. D) Inadvertent intramuscular injection may cause fluctuations in metabolic control. 5. Which of the following observations in a patient would trigger a review or counselling on injection technique? A) Use of long needles for insulin injection. B) Rubbery, lumpy areas of skin used as injection sites. C) Reuse of needles multiple times until pain occurs. D) All the above. Pen needle1 1. Remove pen cap and fit a new needle to the top of the pen. 2. If using cloudy insulin, resuspend by gently rolling and tipping and visually inspecting that it is adequately mixed. 3. Prime the pen by dialling up 1-2 units holding the pen vertically and depressing the plunger. This is repeated until a few drops of insulin are seen, and ensures the pen is working. 4. Dial up the prescribed dose of insulin. 5. Insert needle and push down plunger for 10 seconds (higher doses may require longer). 6. Remove pen needle and discard in sharps bin. 7. Replace pen cap. • If using a skin fold. Lift the skin with the thumb and index or middle finger prior to insertion and don’t release skin fold until needle is removed. • For mixed insulin doses, please see Clinical Guiding Principles for Subcutaneous Injection Technique.1 • Follow manufacturer’s instructions to ensure correct injection technique is abided by. Advising on insulin needle selection and injection technique 2 CPD CREDITS Conclusion Pharmacists have an important role to play in the ongoing education of correct insulin injection technique. Engaging patients about their insulin, specifically their site of administration and correct rotation, angle of administration, use of skin folds, needle length selection, and disposal of sharps, may identify and reduce injecting complications and help optimise treatment outcomes. Pharmacists also have a role in supporting patients who may be anxious about injecting their insulin. All images in this article are published courtesy of Becton Dickinson Pty Ltd and subject to copyright. References 1. Australian Diabetes Educators Association. Clinical Guiding Principles for Subcutaneous Injection Technique. Canberra: 2017 2. Frid AH, Kreugel G, Grassi G, Halimi S, Hicks D, et al. ‘New insulin delivery techniques’. Mayo Clin Proc, 2017; 91 (9): 1231-1255. 3. Frid AH, Hirsch LJ, Menchior AR, Morel DR, Strauss KW. ‘Worldwide injection technique questionnaire study: injecting complications and the role of the professional’. Mayo Clin Proc, 2016; 91 (9): 1224-1230. 4. Gentile S, Strollo F, Ceriello A, AMD-OSDI Injection Technique Study Group. ‘Lipodystrophy in insulin-treated subjects and other injection-site skin reactions: Are we sure everything is clear?’ Diabetes Ther, 2016; 7 (3): 401-409. 5. Australian Medicines Handbook Pty Ltd, January 2020. \\\[Online\\\]. Accessed 6/5/20. Available: https://amhonline.amh.net.au/. 6. Fitter4Diabetes. (2016) Injection techniques questionnaire worldwide results 2014-2015. Accessed 10/5/20. Available: https://www.fitter4diabetes.com/library/ DescriptiveStats.pdf 7. Bahendeka S, Kaushik R, Swai AB, Otieno F, Bajaj S, et al. ‘EADSG guidelines: insulin storage and optimisation of injection technique in diabetes management’. Diabetes Ther, 2019; 10 (2): 341-366. 8. National Diabetes Services Scheme. (2020) Order Form Needles/Syringes. Accessed 8/5/20. Available: https://www.ndss.com.au/wp-content/uploads/order- forms/pen-needles-syringe-order-form.pdf RETAIL PHARMACY • JUL 2020